Executive Summary
| Export | Export | Import | Import | Trade Deficit | Trade Deficit |
| June 2021 N$ 6.9billion | June 2022 N$ 7.9 billion | June 2021 N$ 8.3 billion | June 2022 N$ 10.4 billion | June 2021 N$ 1.4 billion | June 2022 N$ 2.4 billion |
| Top 5 export products | Top 5 Import Products |
| Precious stones (Diamonds) Uranium Fish Non-monetary gold Petroleum oils | Petroleum oils Inorganic chemical elements Civil engineering and contractors Precious stones (Diamonds) Fertilizers |
| Export destination | % Share of Export |
| Botswana South Africa France China Spain | 19.6 18.3 9.0 7.4 6.4 |
| Import Mode of Transport | % Share |
| Road Sea Air Inland Waterways Rail | 52.2 43.5 4.4 0.0 0.0 |
| Main Source of Import for Namibia | % Share of Import |
| South Africa India China Democratic Republic Of Congo Saudi Arabia | 35.3 19.2 7.2 5.5 2.7 |
Analysis
- Total export earnings increased by 26% for June 2022 when compared to that of May 2022. This was influenced by an increase in the exports of petroleum oils, uranium, precious stones (diamonds), ores, and concentrates of base metals
- On an annual basis, total export earnings increased by 15.1 % year on year. This resulted from an increase in the exports earnings recorded for commodities such as precious stones (diamonds), non-monetary gold, petroleum oils, and inorganic chemical elements
- Import bill declined by 15.9% for June 2022 when compared to May 2022. This was attributed to a decline in the import of copper ores and concentrates, sugars, molasses and honey, sulfur and unroasted iron pyrites, civil engineering, and contractors’ equipment
- On an annual basis, the total import bill increased by 24.8 % year on year. This was influenced by an increase in the importation of petroleum oils, inorganic chemical elements, fertilizers, civil engineering, and contractors’ equipment (See figure 1 below)
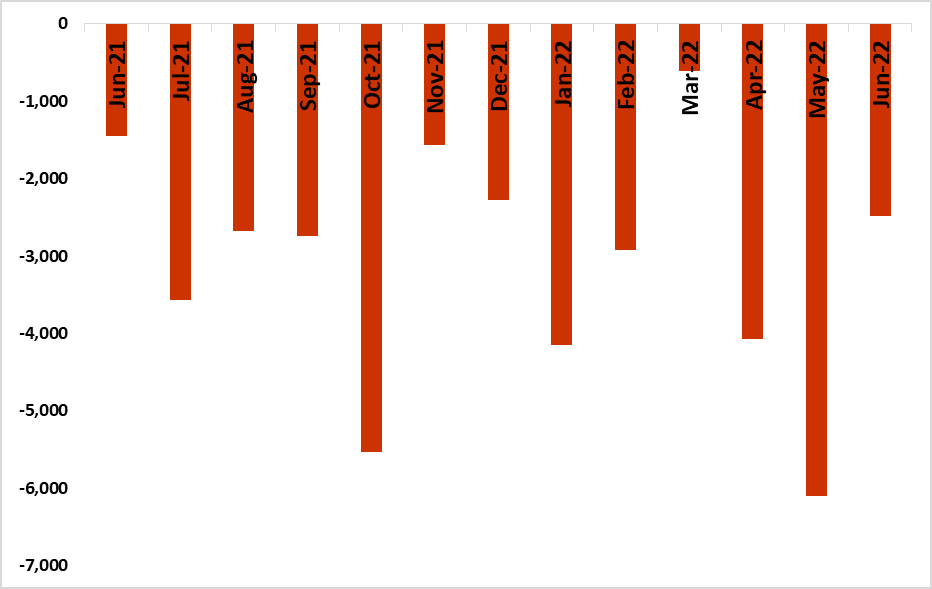
- The trade balance increased by 20.4% for June 2022 in relation to the same period last year (See figure 2)
Figure 1: Export and Import value N$ million, (June 2021 – June 2022)
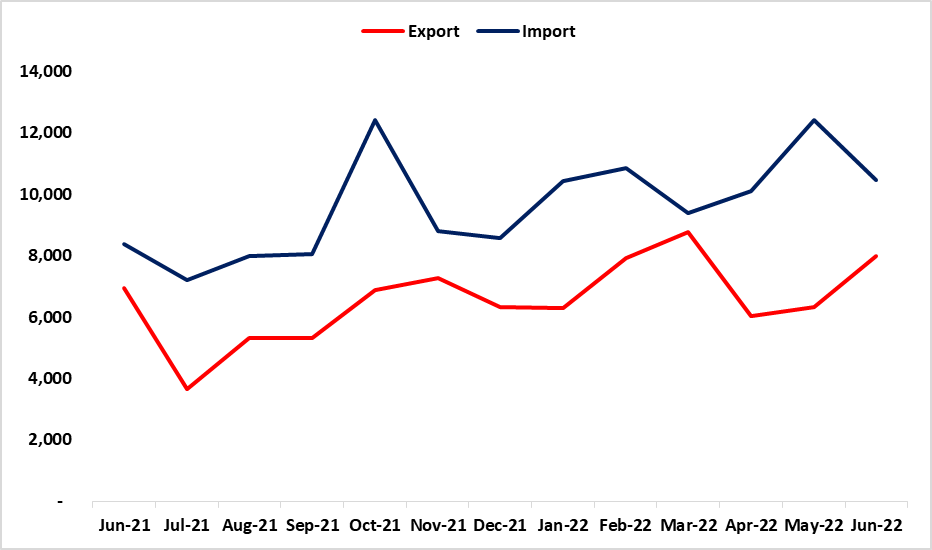
Figure 2: Trade Balance (June 2021 – June 2022)
Outlook
The trade deficit improved in relation to the previous month. This was influenced by a decline in imports augmented by a significant growth recorded for exports. The decline in imports was also influenced by fewer imports of productive assets such as civil engineering and contractor’s equipment which is a reflection of a contraction in the construction sector. The growth recorded in export earnings was influenced by global inflationary pressures augmented by the weaker value of the Rand against the USD for June 2022. The continuous global economic impediments coupled with the foreseen global recession might push the import bill up and hence widen the trade deficit in the short to medium term.