Executive summary
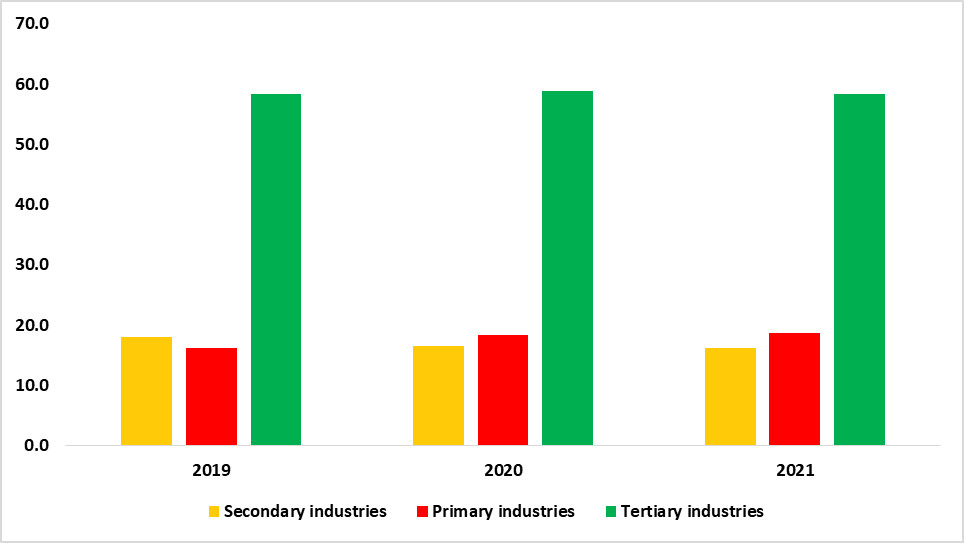
The Namibian economy showed signs of improvement in 2021 after the severe contraction recorded in 2020 due to the negative impact of the Covid-19 pandemic. The domestic economy recorded a recovery of 2.7% in 2021 from a contraction of 8.5% in 2020 (See figure 1 below). The domestic economy revision of 2.7% is an increase from the 2.4% that was recorded in the preliminary national accounts of 2021. The positive performance could be attributed to the relaxation of the restrictive measures that were imposed during the pandemic and a bounce in domestic economic activities. In monetary terms, Real Gross Domestic Product (RGDP) increased to N$ 136.7 billion from N$ 133.2 billion recorded for 2020. The primary and tertiary industries recorded a growth of 6.2% and 1.9% respectively while the secondary industries recorded a decline of 3.3%. The major sectors that attributed to the economy’s rebound were mining, and quarrying, hotels and restaurants, and transport (See figure 2). Namibian economic recovery continues to be driven by the tertiary sector followed by the secondary and primary sectors respectively. (See figure 3).
Analysis
- The mining and quarrying sector registered a growth of 10% in 2021. The surge in the sector was mainly observed in uranium and other mining and quarrying subsectors. During the period under review, the growth recorded for the uranium subsector could be ascribed to an increase in uranium production that emanated from the high global demand for uranium ores. Additionally, growth in the other mining and quarrying subsectors was mainly due to the increase in the production of salt and marble
- The hotels and restaurants sector registered a growth of 8.8% during the period under review, this was due to the relaxation of the Covid-19 travel and gathering restrictions, resulting in high demand for leisure, conferencing, and accommodation services
- The wholesale and retail trade sector registered a growth of 6.1% as a result of an increase in the demand for vehicles, supermarkets, furniture, and wholesale outlets, the sector recorded the first ever growth since 2016
- The health sector registered a growth of 4.3%. The positive performance emanated from an increase in the number of personnel and increased health expenditures
- The professional, scientific, and technical services sectors registered a growth of 2.3%. The first positive performance since 2015. The recovery in the sector came as a result of the relaxation of strict pandemic measures coupled with improved tax compliance regulatory measures (taxpayers paying tax timely and accurately) that have propelled a resurgence in economic activities for the sector
- The transport sector registered a growth of 2.2%. The main subsectors that contributed to the growth were air transport, airport services, port services, and freight transport by road which recorded positive growths of 14.8%, 30.0%, 5.7%, and 3.2%, respectively. This was influenced by an increase in aircraft movement, passenger arrivals, and cargo handled as a result of the easing of the Covid-19 travel restrictions and improved logistical chains
Figure 1: Annual GDP growth rates (2010 – 2021)
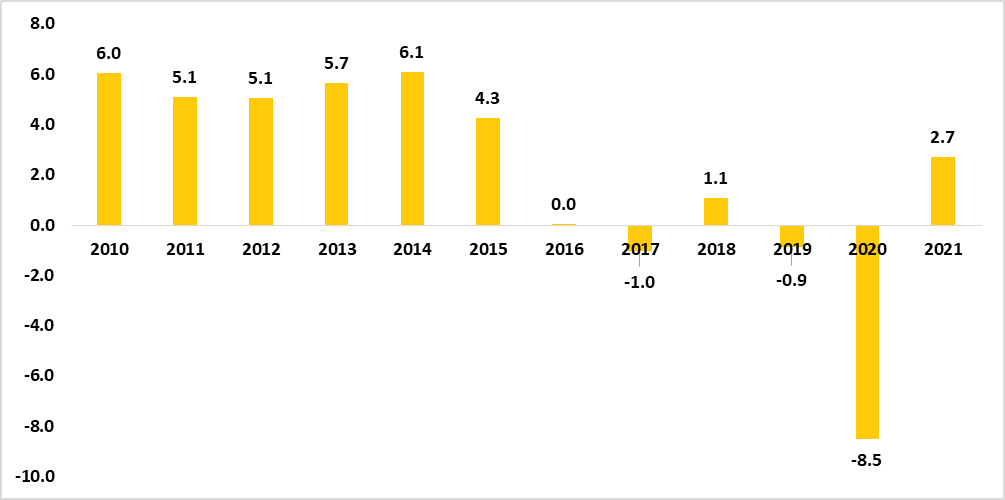
Figure 2: GDP Growth per sector (2020 & 2021)
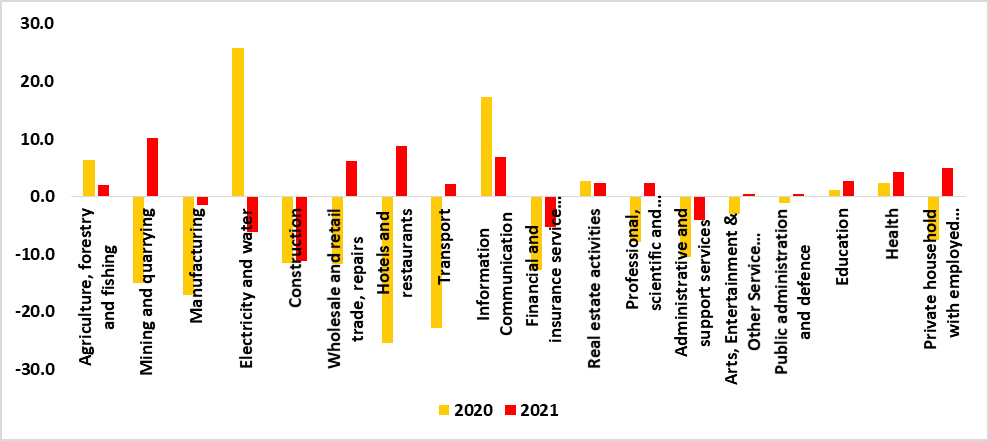
Figure 3: Industries’ contribution to GDP (2019 – 2021)
Outlook
The growth of the Namibian economy is intertwined with the performance of the South African economy. South Africa’s GDP declined by 0.7% in quarter 2 of 2022 due to devastating floods in KwaZulu-Natal and continuous load shedding which had a negative impact on a number of industries, most notably manufacturing. As such Namibia’s GDP could be negatively affected as the country obtains most of its imports from South Africa. Hence, Namibia should strive and enhance its manufacturing industries to create more local enterprises. We anticipate a moderate recovery for the remaining of 2022 on the back of the anticipated recession in the advanced economies.